History of AI
75 years of AI evolution
How AI Works
Understanding AI fundamentals
AI Agents
Autonomous AI systems
AI Evolution (1950 - 2026)
Timeline Navigator
Hover milestones to move across 1950 to 2026.
- OpenAI GPT-5.3 Codex released
- Anthropic Claude Opus 4.6 released
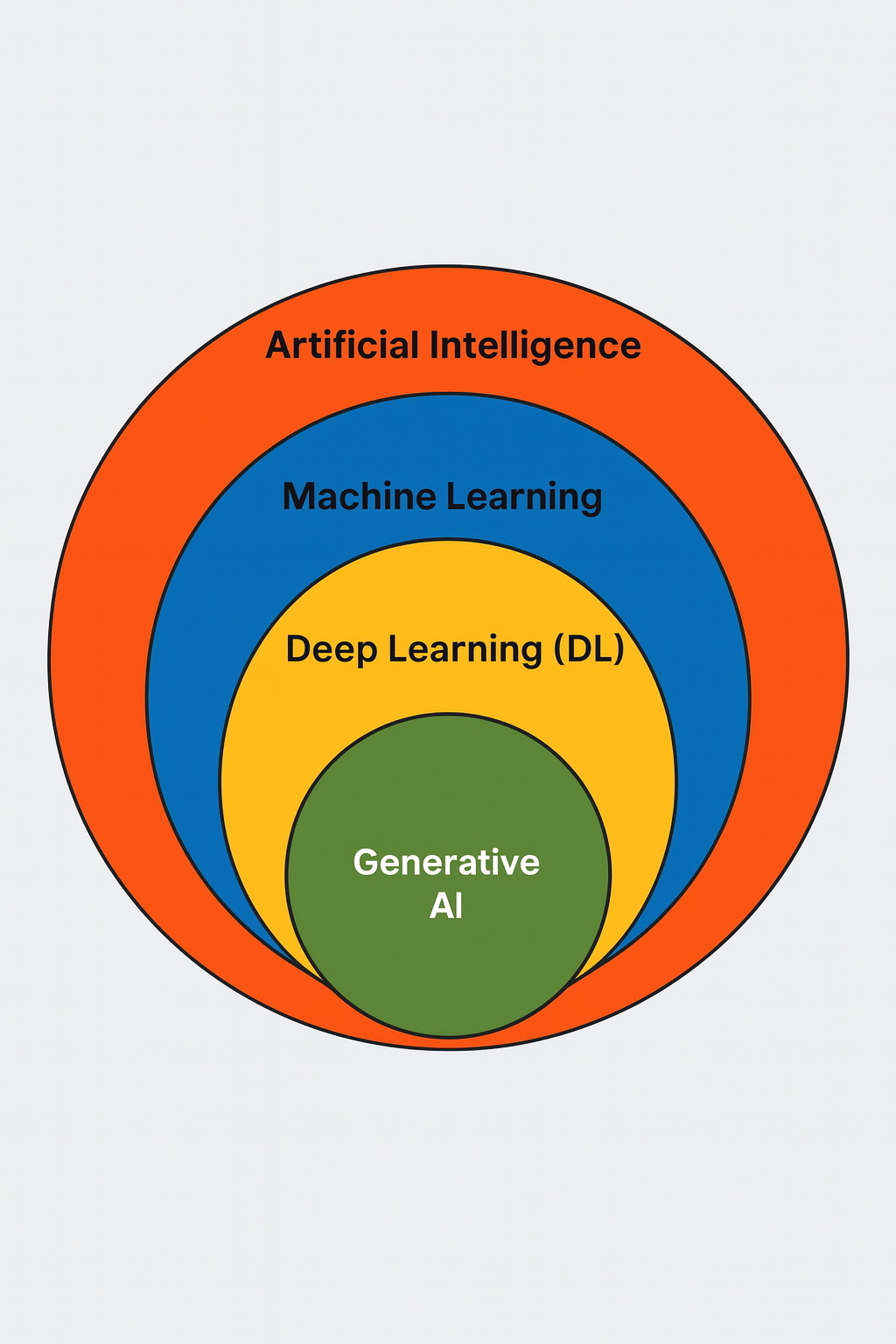
Artificial Intelligence aims to mimic human intelligence in machines. Machine Learning learns from data to make predictions (weather forecasting). Deep Learning (face recognition) uses neural networks inspired by the human brain to improve those predictions. Generative AI (LLMs like ChatGPT) goes a step further by creating entirely new content. LLMs means Large Language Models.
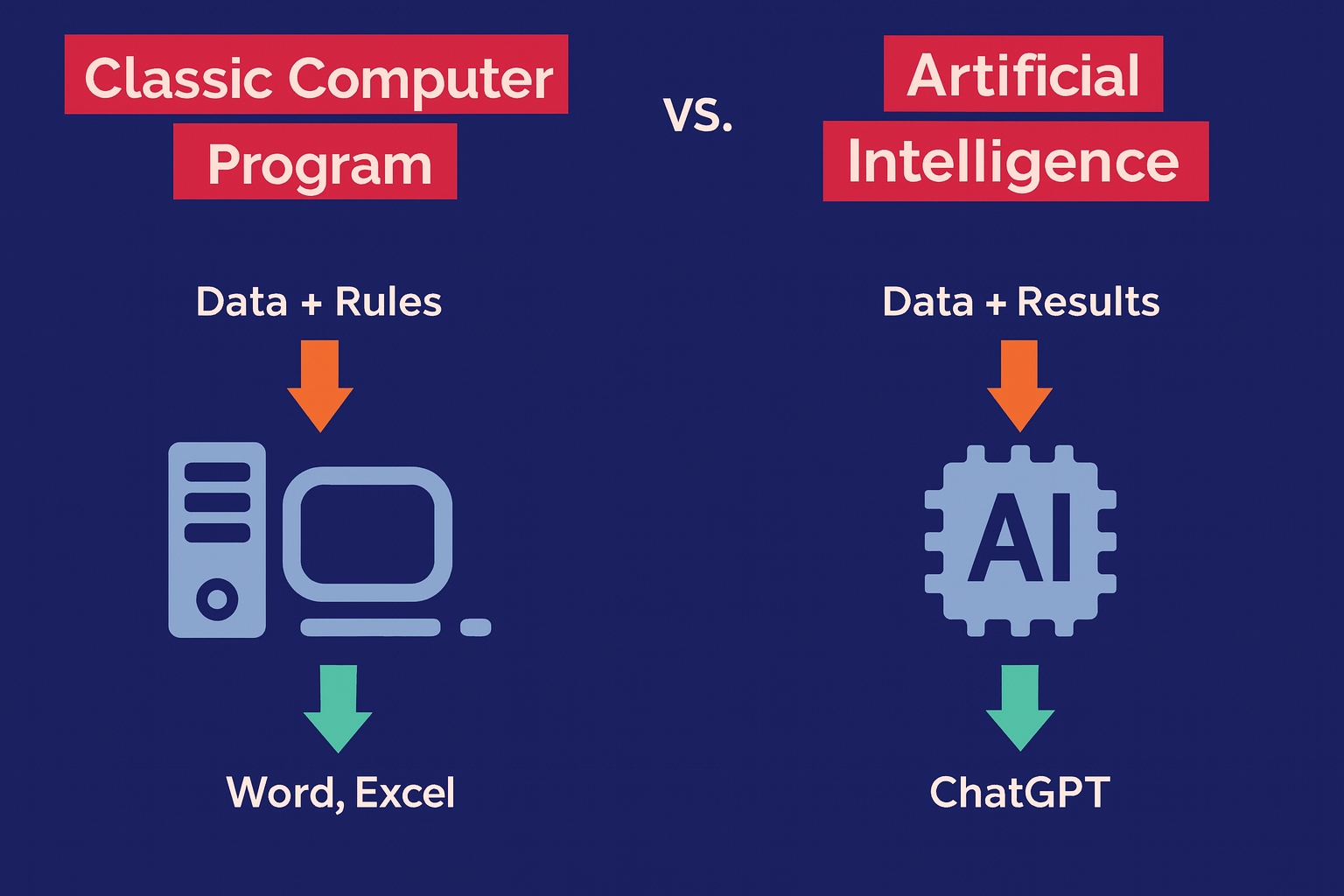
A classic computer program follows fixed rules written by humans to
produce predictable outputs
(for example, Excel formulas or a calculator).
Artificial Intelligence learns from data and examples, allowing it to
generate answers, adapt, and assist
(for example, ChatGPT writing an email or answering
questions).
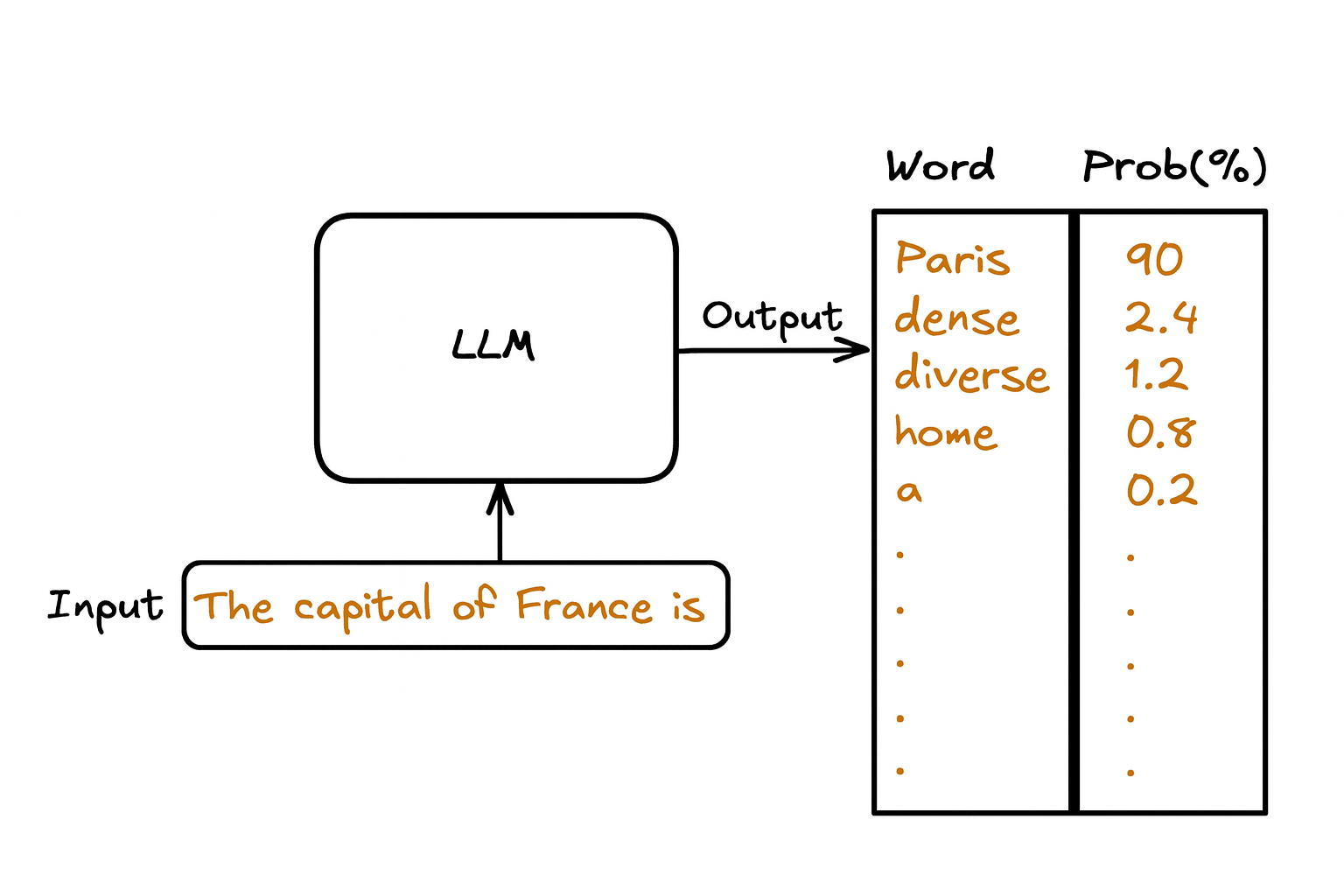
An LLM reads your input and predicts the most likely next word based on
probabilities learned from massive data.
It generates text by repeatedly choosing the highest-probability word, forming fluent
answers like "Paris."
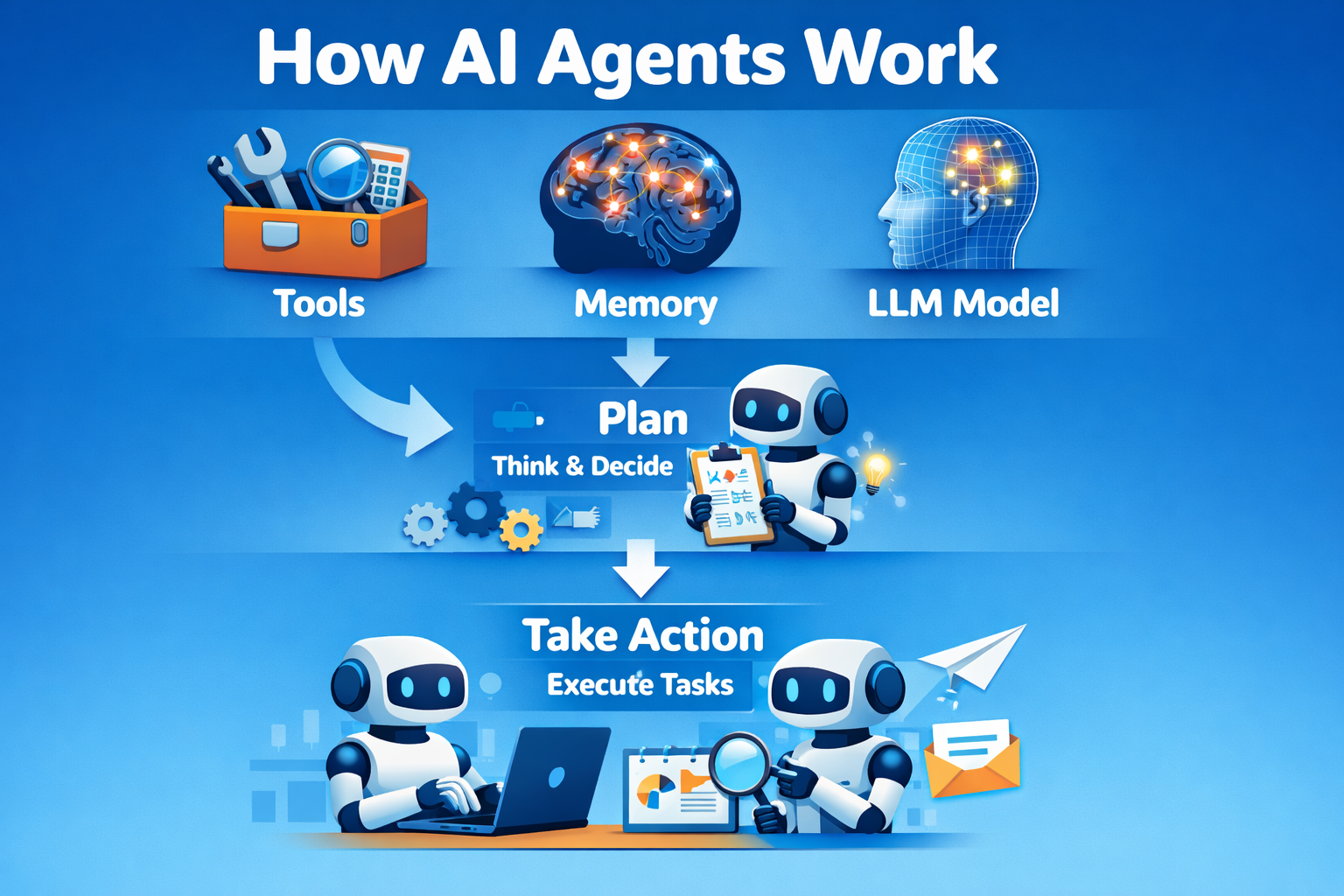
AI Agents combine an LLM with tools and memory to think, plan, and
decide what to do next.
Unlike simple LLMs that only respond with text, agents can plan steps and take
real actions to complete tasks.